Capacitive vs Resistive Touch Screen Pros and Cons: Your 2025 Guide to Choosing the Right Technology
News
Jun-22-2025
Have you ever tried swiping on your phone with gloves on and gotten no response? Or maybe you’ve used an ATM where you had to press hard to make it work? That’s the difference between capacitive and resistive touch screens in action. These two types of touch screen technology power everything from smartphones to industrial kiosks, but each has unique strengths and weaknesses. Understanding the capacitive vs resistive touch screen pros and cons helps you pick the right tech for your phone, tablet, or business project. Let’s break it down in a simple, friendly way with real-world examples to guide your choice in 2025!
Everyday Examples of Touch Screens
Picture yourself zooming in on a photo with a quick pinch on your phone—that’s a capacitive touchscreen making it smooth and easy. Now think about tapping a factory control panel or an ATM that needs a firm push—that’s likely a resistive touchscreen. Both are everywhere, but they’re built for different jobs. Whether you’re choosing a new device or designing one, knowing the pros and cons of touchscreens ensures you get the best user experience. Ready to explore the resistive vs capacitive comparison? Let’s dive in!
Basic Overview: What Is a Capacitive Touch Screen?
A capacitive touch screen detects your touch using electrical charges. It has a conductive glass layer that senses your finger or a special stylus, responding to light touches. This makes it super fast and perfect for gestures like pinching or swiping. You’ll find capacitive screens in smartphones, tablets, and car displays because they’re responsive and clear.
Why Capacitive Screens Are So Common
Their speed and multi-touch support make them a favorite for modern, user-friendly devices.
How They Fit in Daily Life
From phones to laptops, capacitive screens deliver a smooth user experience for everyday tasks.
Basic Overview: What Is a Resistive Touch Screen?
A resistive touch screen works with pressure-based input. It uses two flexible layers that touch when you press, completing a circuit to register your input. You can use your finger, a stylus, or even a gloved hand—anything that applies pressure works. These screens are tough and versatile, often found in ATMs, factory machines, or delivery tablets.
Resistive Screen Versatility
Their stylus support and glove compatibility make them ideal for settings where flexibility matters.
Common Applications
Resistive screens are used in places where durability trumps fancy gestures, like industrial controls.
How Capacitive Screens Work
Capacitive screens rely on an electrical field created by a conductive glass layer, usually indium tin oxide (ITO). When your finger touches the screen, it disrupts this field because your body conducts electricity. Sensors pinpoint the exact spot, and the device responds instantly, like opening an app. Think of it as dropping a pebble in a pond—the ripples show where you touched. For a deeper dive, see How capacitive touch screens work.
The Role of Conductivity
Your finger’s electrical charge triggers the touchscreen sensor, making it fast and precise.
Why They Feel So Smooth
Light touches are enough, ensuring quick responses without lag.
How Resistive Screens Work
Resistive screens have two thin, flexible layers separated by a tiny gap. When you press, the layers touch, creating a circuit that tells the device where you pressed. It’s like pressing two sheets of plastic together to make a connection. This pressure-based input works with any object, from a stylus to a gloved finger, but it needs more force than capacitive screens.
Simple Design, Reliable Results
The straightforward design makes resistive screens dependable in tough conditions.
Pressure-Based Mechanics
Pressing hard ensures the layers connect, but it can feel clunky compared to capacitive.
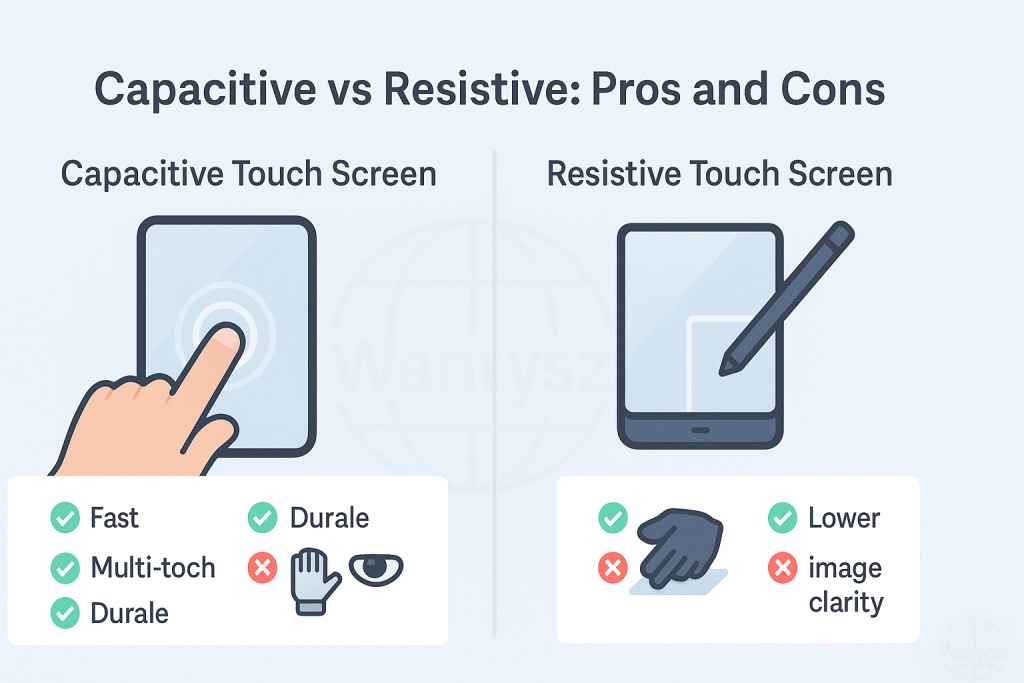
Capacitive Touch: Pros
Capacitive touchscreens have big advantages that make them popular:
- Multi-Touch Support: Pinch, zoom, or swipe with multiple fingers—perfect for smartphones and tablets.
- High Clarity Display: The conductive glass lets more light through, creating bright, vivid visuals.
- Responsive User Experience: Light touches trigger instant responses, great for gaming or typing.
- Durable Glass Surface: Resists scratches and holds up under daily use, ensuring screen durability.
These pros and cons of touchscreens make capacitive screens a top pick for consumer tech. Learn more at Advantages of capacitive touch screens.
Vibrant Visuals
The high clarity display makes photos, videos, and apps look stunning.
Speed for Everyday Use
Capacitive screens are fast, making tasks like texting or scrolling feel effortless.
Long-Lasting Design
The durable glass surface keeps screens looking new even after heavy use.
Capacitive Touch: Cons
Capacitive screens have some drawbacks to consider:
- Poor Glove Compatibility: Regular gloves block the electrical field, though some PCAP screens support special gloves.
- Limited Rugged Performance: Less suited for extreme dust or water in rugged environments.
- Higher Cost: More expensive than resistive screens, especially for large or custom designs.
These cons can limit capacitive screens in certain scenarios.
Challenges with Gloves
Cold weather or industrial settings often require gloves, where capacitive struggles.
Cost Implications
Higher capacitive touchscreen costs can be a hurdle for budget-conscious projects.
Environmental Sensitivity
Rain or wet fingers can disrupt touch accuracy on capacitive screens.
Resistive Touch: Pros
Resistive touchscreens shine in specific situations:
- Stylus and Glove Support: Works with any object, including gloves or pens, offering great stylus support.
- Lower Cost: Cheaper to produce, making them budget-friendly for simple devices.
- Dust and Water Resistance: Handles rugged environments like factories or outdoor kiosks well.
- Ideal for Industrial Use: Reliable in settings needing glove compatibility or durability.
These strengths make resistive screens a solid choice for tough applications.
Input Flexibility
Any object, from a pen to a gloved finger, works, making resistive screens versatile.
Rugged Environment Fit
They resist dust and water, perfect for harsh conditions like construction sites.
Budget-Friendly Option
Lower costs make resistive screens appealing for high-volume, simple devices.
Resistive Touch: Cons
Resistive screens have notable downsides:
- No Multi-Touch: Usually limited to single-touch, missing out on gestures like zooming.
- Requires Pressure: Needs a firm press, which feels less intuitive than capacitive.
- Poorer Display Clarity: Extra layers dim the screen, reducing visual quality.
- Less Responsive Over Time: Wear from constant pressing can reduce touch accuracy.
These cons make resistive screens less ideal for modern consumer gadgets.
Limited Gesture Support
Lack of multi-touch restricts resistive screens to basic inputs like button presses.
Visual Quality Drawbacks
Dimmer displays can make text or images harder to see in bright light.
Wear and Tear Issues
Repeated pressure can wear out layers, impacting screen durability over time.
Side-by-Side Comparison Table
Here’s a clear capacitive vs resistive touchscreen comparison:
| Feature | Capacitive Touchscreen | Resistive Touchscreen |
|---|---|---|
| Touch Method | Electrical charge (finger/stylus) | Pressure (any object) |
| Multi-Touch | Yes (pinch, zoom, swipe) | Rarely (single-touch) |
| Display Clarity | High, vibrant | Moderate, dimmer |
| Responsiveness | Very fast, light touch | Slower, needs pressure |
| Durability | Scratch-resistant glass | Wears with pressure |
| Glove Compatibility | Limited (special gloves for PCAP) | Excellent |
| Cost | $20–$2,000 | $10–$500 |
| Best Use | Smartphones, tablets, indoor | Factories, ATMs, outdoor |
This table highlights the pros and cons of touchscreens for quick decision-making.
Touch Accuracy and Sensitivity
Capacitive screens are champs at touch accuracy. Their conductive glass detects light touches precisely, making them ideal for detailed tasks like drawing or typing on a phone. You tap an icon, and it responds instantly. Resistive screens, Juno, with pressure-based input, are less accurate. Pressing hard can cause slight misreads, especially on worn screens, making them less precise for small targets.
Capacitive Precision Advantage
Perfect for apps requiring fine control, like digital sketching.
Resistive Accuracy Limits
Better for broad inputs, like menu selections, but less precise for detailed tasks.
Sensitivity Differences
Capacitive’s light-touch detection feels smoother than resistive’s firm press.
Environmental Suitability: Indoor vs Outdoor
Capacitive screens excel indoors, where their high clarity display shines in controlled lighting. Outdoors, rain or wet fingers can disrupt the electrical field, causing misreads. Resistive screens are better for rugged environments. Their pressure-based input resists dust and water, and they work with gloves, making them ideal for outdoor kiosks or factories.
Capacitive Indoor Strength
Bright, clear visuals suit offices, homes, or retail settings.
Resistive Outdoor Edge
Glove compatibility and water resistance make resistive screens outdoor-friendly.
Weather Impact
Capacitive screens struggle in wet conditions, while resistive screens handle them well.
Durability and Maintenance
Capacitive screens have a durable glass surface that resists scratches, requiring minimal maintenance—just a wipe with a microfiber cloth. Resistive screens, with flexible layers, wear out from repeated pressure, needing replacements sooner. Their screen durability is strong in harsh conditions but degrades over time.
Capacitive Longevity
The glass surface withstands heavy use without losing clarity.
Resistive Maintenance Needs
Worn layers may need replacing, increasing long-term costs.
Cleaning Considerations
Capacitive screens are easier to clean, while resistive screens can trap dirt in layers.
Use Case Matchups: Consumer vs Industrial
Each technology suits different needs:
- Consumer Devices: Capacitive screens dominate smartphones, tablets, and laptops for multi-touch support and high clarity displays. Examples: iPhones, iPads, car infotainment systems.
- Industrial Settings: Resistive screens excel in factories, ATMs, and medical devices for glove compatibility and rugged environment durability. Examples: control panels, delivery tablets.
Consumer Device Appeal
Capacitive screens offer a premium user experience for personal gadgets.
Industrial Reliability
Resistive screens handle tough conditions with stylus support and durability.
Hybrid Solutions
Some PCAP capacitive screens offer glove compatibility, bridging the gap.
When Capacitive is the Better Choice
Choose a capacitive touchscreen when:
- You need multi-touch for gestures like pinching, zooming, or swiping.
- A high clarity display is key for videos, gaming, or design.
- You want a smooth, responsive user experience for consumer devices.
- The device is used indoors or in controlled environments.
Capacitive screens are ideal for phones, tablets, and modern kiosks. Learn more at Advantages of capacitive touch screens.
Best for Consumer Tech
Capacitive screens make smartphones and tablets intuitive and vibrant.
Ideal Settings
They shine in clean, indoor environments with frequent use.
Premium Features
Multi-touch and clarity justify the higher cost for consumer applications.
When Resistive is Still the Best Option
Opt for a resistive touchscreen when:
- Glove compatibility or stylus support is needed, like in cold or industrial settings.
- The device faces dust, water, or extreme conditions in a rugged environment.
- Budget is a concern, as resistive screens are cheaper.
- Single-touch inputs are enough, like for ATMs or control panels.
Resistive screens are perfect for factories, outdoor kiosks, or medical equipment.
Industrial Advantages
Resistive screens thrive where screen durability and input flexibility are critical.
Budget-Friendly Choice
Lower costs make resistive ideal for simple, high-volume applications.
Specific Use Cases
They’re great for tasks like signing delivery tablets with a stylus.
Custom Solutions for Special Environments
Both technologies offer custom options. Projected capacitive touch (PCAP) screens can be tailored for glove compatibility or water resistance, ideal for outdoor or medical uses. Resistive screens can be customized for precise stylus support in industrial settings. Custom solutions ensure the right fit for unique needs. Explore Capacitive touch custom screen for more.
PCAP Customization
PCAP screens add multi-touch and rugged features for specialized applications.
Resistive Customization
Custom resistive screens enhance pressure-based input for specific tasks.
Tailored Solutions
Customization bridges gaps, like adding glove support to capacitive screens.
Cost Comparison and Budget Considerations
Cost is a big factor in the resistive vs capacitive comparison:
- Capacitive: $20–$2,000. Higher due to advanced conductive glass and multi-touch support.
- Resistive: $10–$500. Cheaper, simpler manufacturing for pressure-based input.
Capacitive screens are pricier but offer premium features. Resistive screens save money for budget projects.
Capacitive Premium Pricing
Higher costs reflect touch accuracy and high clarity displays.
Resistive Cost Savings
Affordable for basic devices, like industrial controls or ATMs.
Long-Term Cost Impacts
Capacitive’s screen durability reduces replacement costs over time.
Final Comparison Chart Recap
| Aspect | Capacitive | Resistive |
|---|---|---|
| Pros | Multi-touch, clear display, responsive, durable glass surface | Glove/stylus support, low cost, rugged, dust/water-resistant |
| Cons | Poor glove compatibility, less rugged, expensive | No multi-touch, needs pressure, dimmer display, wears out |
| Best For | Smartphones, tablets, indoor use | Factories, ATMs, outdoor kiosks |
| Cost | $20–$2,000 | $10–$500 |
This chart sums up the capacitive vs resistive touch screen pros and cons.
Conclusion: Choose Based on Your Use Case and Environment
The capacitive vs resistive touch screen pros and cons show each technology has a unique role in 2025. Capacitive touchscreens lead for consumer devices like phones and tablets, thanks to multi-touch support, high clarity displays, and touch accuracy. Resistive touchscreens are best for rugged environments like factories or ATMs, offering glove compatibility, stylus support, and lower costs. Your choice depends on your priorities: a smooth user experience or durability in tough conditions.
For consumer tech, go capacitive for vibrant, responsive displays. For industrial or outdoor use, resistive is hard to beat. Custom options, like glove-compatible PCAP, can meet specific needs. Ready to decide? Explore Capacitive touch screen use cases or contact a supplier to find the perfect touchscreen for your project.
Related Topics

Capacitive Touch Integrated Touchscreen: 2025 Technology
Aug-25-2025

Capacitive Touch Screen POS Terminal – Next-Gen Solutions
Aug-25-2025

Capacitive Touch HMI Interface | Durable & Ergonomic Control
Aug-24-2025

Capacitive Panel OEM Manufacturers – Custom Touchscreen Solutions
Aug-24-2025
Get a Free Quote
✔ 16 Years Manufacture Service ★★★★★
✔ 3 Technical Experts And 52+ Project Engineers Will Assiste You
✔ Wanty Employs Over 52 Engineers, Many Of Whom Come From Leading Tft Lcd Module Companies Such As Tianma And Boe-Varitronix. Each Core Team Member Brings 15 Years Of Industry Experience.
✔ If you would like more information about our products and services, please contact us. Whether you need a standard solution or a customized one, we are here to meet your needs.
✔ Please complete the form below, and the selected location will contact you promptly. Thank you for visiting, and have a great day!
