How Capacitive Touch Screens Work: Your Complete Guide to Touchscreen Technology
News
Jun-22-2025
Imagine tapping your phone to send a text or swiping through photos on a tablet. That smooth, instant response? It’s all thanks to capacitive touch screen technology. These screens power our favorite devices, making every interaction feel effortless. But how does a capacitive touch screen turn your touch into action? Why is it so fast and reliable? In this beginner-friendly guide, we’ll explain capacitive sensing in simple terms, using clear analogies to break down the tech behind touchscreen sensors. From smartphones to kiosks, you’ll see why this technology rules in 2025. Let’s dive in and uncover the magic of touch input detection!
Why Understanding Capacitive Touch Screens Matters
Capacitive touch screens are everywhere—your phone, car dashboard, even the self-checkout at the grocery store. Knowing how they work helps you appreciate the tech that makes life easier. Whether you’re a curious user, a student, or a business exploring touch technology, this guide demystifies capacitive touch screen technology. Want to start with the basics? Check out What is a capacitive touch screen for a quick primer.
The Impact of Touch Technology
From gaming to medical devices, capacitive sensing shapes how we interact with the world. Understanding it opens doors to smarter tech choices.
Why It’s Relevant in 2025
With foldable phones and wearable devices on the rise, touchscreen sensors are more critical than ever, driving innovation across industries.
Basic Principles of Capacitive Sensing
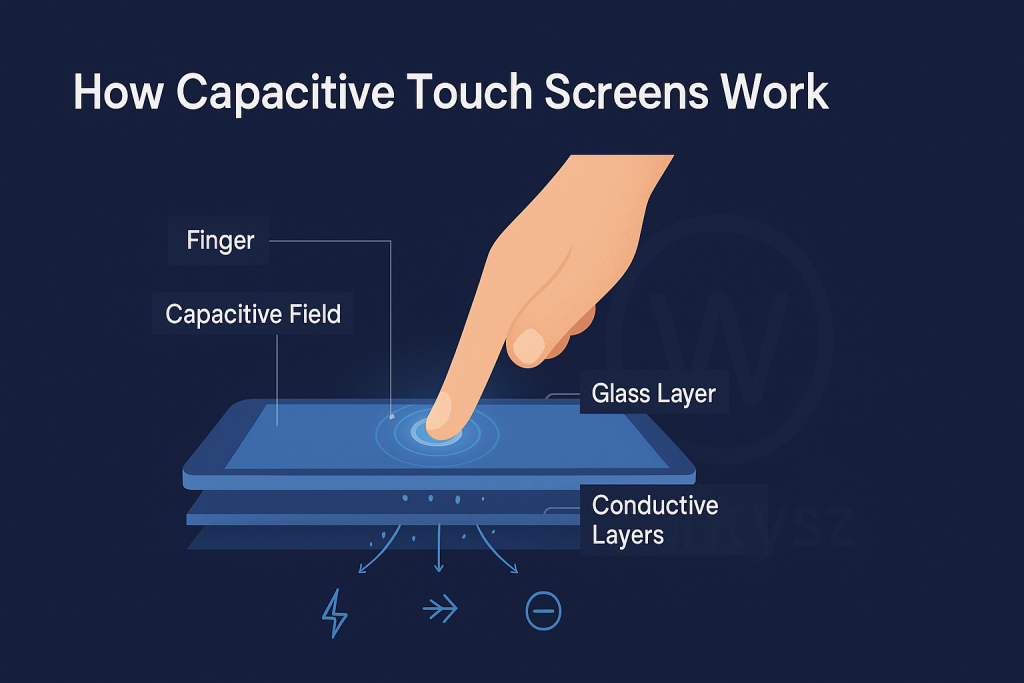
Capacitive sensing is all about detecting changes in an electrical field. A capacitive touch screen creates a steady electric field across its surface. When your finger touches it, it disrupts that field because your body conducts electricity. Sensors pick up this change and figure out exactly where you touched.
Picture the screen as a calm pond. Your finger is a pebble that creates ripples, and the screen “sees” those ripples to know where the pebble landed. This process is super fast, making capacitive screens ideal for quick, precise interactions.
What is Capacitance?
Capacitance is the ability to store an electrostatic charge. Your finger alters this charge when you touch, triggering the touchscreen sensor to respond.
The Role of Conductivity
Capacitive screens need a conductive object, like your finger or a special stylus, to disrupt the electrical field. Non-conductive items, like regular gloves, won’t work.
Components of a Capacitive Touch Screen
A capacitive touch screen is like a high-tech sandwich with these key parts:
- Glass Surface: A tough, clear layer that protects the screen and feels smooth to the touch.
- Conductive Layer: Usually indium tin oxide (ITO), a transparent conductor that creates the electrical field.
- Sensors: Tiny detectors that notice changes in the field when you touch.
- Controller Chip: The brain that processes touch data and sends commands, like opening an app.
- Protective Coating: Reduces smudges, scratches, and glare for a better user interface.
These components team up to make the screen responsive, clear, and durable.
The Glass Surface
The glass ensures durability and lets light through for bright, vivid displays. It’s often treated to resist fingerprints and wear.
The Conductive Layer’s Role
The conductive layer is the core of capacitive touch screen technology, maintaining the electric field that detects your touch.
Sensors and Controllers
Sensors spot changes in the electrostatic charge, while the controller chip translates them into actions, ensuring a seamless experience.
How Your Finger Interacts with the Screen
When you touch a capacitive screen, your finger acts as a conductor. It disrupts the screen’s electrical field at the point of contact, changing the electrostatic charge. Sensors detect this change and map the exact spot you touched. The controller chip then turns this data into an action, like tapping an icon or swiping a page.
Think of the screen as a grid of invisible lines. Your finger messes up the pattern of those lines, and the screen pinpoints where the disruption happened. This happens in milliseconds, so it feels instant.
Why Fingers Are Key
Your body’s natural conductivity makes fingers perfect for touch input detection. Special styluses mimic this for tasks like drawing or writing.
Non-Conductive Limits
Objects like plastic pens or regular gloves don’t affect the electrical field, so they won’t trigger the screen.
Projected Capacitive Touch Technology Explained
Projected capacitive touch (PCAP) is the most advanced type of capacitive touchscreen. It uses a sensor grid of electrodes in the conductive layer to create a precise electrical field. This grid lets PCAP screens detect multiple touches at once and even work through thick glass or gloves in some cases.
PCAP powers the smooth multi-touch detection in your smartphone. It’s also used in rugged settings, like outdoor kiosks, because it’s durable and accurate. Curious about other touchscreen types? See Capacitive vs resistive touch screen for a comparison.
How PCAP Functions
The sensor grid forms a coordinate system, like a map. When you touch, the screen tracks your finger’s location on this map, even with multiple fingers.
PCAP’s Rugged Capabilities
PCAP’s ability to work in rain or with gloves makes it ideal for industrial displays, medical devices, and public touchscreens.
Surface Capacitive vs Projected Capacitive: Key Differences
Capacitive touchscreens come in two main flavors: surface capacitive and projected capacitive. Here’s how they differ:
- Surface Capacitive:
- Uses a single conductive layer for touch detection.
- Simpler and cheaper, but less precise.
- Best for single-touch devices, like basic kiosks or ATMs.
- Less common in 2025 due to limited features.
- Projected Capacitive (PCAP):
- Uses a sensor grid for precise, multi-touch detection.
- More advanced, used in smartphones, tablets, and high-end displays.
- Works through thicker materials and supports complex gestures.
- The standard for modern user interfaces.
PCAP dominates because of its versatility, but surface capacitive has niche uses.
Surface Capacitive Applications
Surface capacitive is cost-effective for simple, single-touch devices where precision isn’t a priority.
PCAP’s Edge in Modern Tech
PCAP’s accuracy and multi-touch detection make it the go-to for devices requiring smooth, complex interactions.
Multi-touch Capability: How Multiple Touches Are Detected
Multi-touch detection is a standout feature of capacitive touchscreens. It lets you use multiple fingers to pinch, zoom, rotate, or swipe. PCAP screens make this possible with their sensor grid, which tracks each touch point independently.
For example, when you pinch to zoom on a map, the screen detects two fingers moving apart and adjusts the view. The conductive layer and sensors map these touches in real time, creating a fluid experience.
The Sensor Grid’s Role
The sensor grid acts like a chessboard, tracking multiple “pieces” (your fingers) at once, enabling gestures without confusion.
Gesture Recognition
Advanced capacitive sensing recognizes patterns, like a three-finger swipe, making devices more intuitive for gaming or creative apps.
Signal Processing: From Touch to Action
Turning a touch into an action involves a few steps:
- Touch Detection: The sensor grid spots a change in the electrical field.
- Data Collection: Sensors send the touch location to the controller chip.
- Processing: The chip maps the touch to coordinates on the screen.
- Action: The device’s software translates the coordinates into a command, like opening an app.
This process is so fast—happening in milliseconds—that you don’t notice the steps.
The Controller Chip’s Job
The controller chip is like a translator, turning raw touch data into instructions the device can act on.
Software’s Role
Operating systems like iOS or Android work with the chip to ensure every tap, swipe, or pinch feels seamless.
Advantages of Capacitive Sensing Compared to Other Technologies
Capacitive touchscreens outperform other technologies, like resistive touchscreens, in several ways:
- High Sensitivity: Detects light touches for a smooth, responsive user interface.
- Multi-touch Support: Handles gestures like pinching, zooming, or swiping.
- Vivid Displays: The transparent conductor allows bright, clear visuals.
- Durability: Glass surfaces resist scratches and wear.
- Slim Design: Enables thin, lightweight devices.
- Energy Efficiency: Uses less power for touch input detection.
For a deeper dive into these benefits, check out Advantages of capacitive touch screens.
Capacitive vs Resistive
Unlike resistive screens, which need pressure and have dimmer displays, capacitive screens offer speed and clarity.
Why Consumers Love Capacitive
The premium feel of capacitive screens makes them a favorite for personal devices, enhancing everyday interactions.
Common Use Cases of Capacitive Touch Screens
Capacitive touchscreens are incredibly versatile. Here’s where you’ll find them:
- Smartphones and Tablets: Smooth multi-touch detection for iPhones, Androids, and iPads.
- Laptops: Touchscreen laptops for navigation, drawing, or creative tasks.
- Car Displays: Infotainment systems for GPS, music, and climate controls.
- Kiosks: Self-service machines at airports, restaurants, or retail stores.
- Medical Devices: Precise, clear screens for patient monitors and diagnostic tools.
- Gaming Consoles: Responsive controls for devices like the Nintendo Switch.
- Smart Home Devices: Thermostats and hubs with sleek, touch-based controls.
For more examples, explore Capacitive touch screen use cases.
Consumer Device Dominance
Capacitive screens are standard in personal tech because of their speed, clarity, and intuitive gestures.
Industrial and Public Applications
PCAP screens excel in rugged settings, like factory displays or outdoor kiosks, due to their durability and accuracy.
Challenges and Limitations
Capacitive touchscreens aren’t perfect. Here are some challenges:
- Glove Incompatibility: Regular gloves block the electrostatic charge, though PCAP can work with special gloves.
- Water Sensitivity: Wet screens can misread touches, like in rain or with sweaty fingers.
- Higher Cost: More expensive than resistive screens, especially for custom designs.
- Fragility: Glass can crack if dropped, unlike flexible resistive screens.
Advances are addressing these issues, but they’re worth considering.
Tackling Water Sensitivity
New sensor grids are better at distinguishing between water and intentional touches, improving outdoor use.
Glove Compatibility Solutions
PCAP screens with adjustable sensitivity are making glove use easier, especially in cold or industrial environments.
Custom Capacitive Touch Screen Solutions
Need a touchscreen that’s one-of-a-kind? Custom capacitive screens can be tailored for specific needs. From curved displays for car dashboards to rugged screens for outdoor kiosks, manufacturers can adjust size, shape, sensitivity, or durability. PCAP screens, for instance, work through thick glass or gloves, perfect for tough settings.
Custom solutions are ideal for businesses creating innovative products or specialized equipment. Want to explore options? Check out Capacitive touch custom screen for tailored designs.
Benefits of Customization
Custom screens let you create unique, user-friendly products, whether for a futuristic gadget or a heavy-duty machine.
Examples of Custom Designs
Think giant interactive museum displays or compact screens for wearable medical devices—custom touchscreen sensors make it possible.
Future Developments in Capacitive Touch Technology
Capacitive touchscreens are evolving rapidly. Here’s what’s coming in 2025 and beyond:
- Foldable Screens: Flexible transparent conductors for foldable phones and tablets.
- Wearable Tech: Tiny, curved touchscreen sensors for smartwatches and fitness trackers.
- AR/VR Integration: Capacitive sensing in augmented reality glasses for intuitive controls.
- Haptic Feedback: Screens that “feel” like buttons when touched, enhancing the user interface.
- Eco-Friendly Materials: Sustainable conductive layers to reduce environmental impact.
- Advanced Gestures: Smarter multi-touch detection for custom gestures in creative apps.
These trends are pushing capacitive touch screen technology to new heights.
Sensitivity Improvements
Enhanced sensor grids are boosting accuracy, enabling finer control for drawing or complex interactions.
Flexible Display Innovations
Materials like silver nanowires are replacing ITO, making screens bendable for innovative designs like foldable devices.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
Producing conductive layers and glass can be resource-heavy. Manufacturers are now using recycled materials and energy-efficient processes to reduce the environmental impact. For durability, glass screens resist scratches but can crack, so proper care, like using screen protectors, extends their life.
Eco-Friendly Advances
Sustainable coatings and recyclable components are making touch technology greener, aligning with 2025’s focus on sustainability.
Durability Tips
Regular cleaning with a microfiber cloth and avoiding drops keep touchscreen sensors in top shape.
Choosing the Right Capacitive Touch Screen
Picking the perfect capacitive touchscreen depends on your needs:
- Environment: Outdoor or glove-heavy settings? PCAP is best for rugged use.
- Size and Shape: Custom screens can fit unique designs, like curved or large displays.
- Durability Needs: Opt for toughened glass for high-traffic devices.
- Budget: Balance cost with features like multi-touch detection or high clarity.
Work with a trusted manufacturer to find the right solution for your project.
Questions to Ask Manufacturers
Ask about touch sensitivity, durability, and customization to ensure the screen meets your goals.
Conclusion: Why Capacitive Touch is the Standard Today
Capacitive touchscreens are the backbone of modern devices, delivering fast, clear, and intuitive user interfaces. With capacitive sensing, a transparent conductor, and multi-touch detection, they make every tap and swipe feel effortless. From smartphones to industrial displays, touchscreen sensors power our connected world in 2025. Despite challenges like glove incompatibility, innovations like PCAP and flexible screens are keeping capacitive tech ahead of the curve.
Understanding how capacitive touch screen technology works shows why it’s the top choice for consumers and businesses alike. It’s not just a screen—it’s the bridge between you and your digital life.
Related Topics

Capacitive Touch Integrated Touchscreen: 2025 Technology
Aug-25-2025

Capacitive Touch Screen POS Terminal – Next-Gen Solutions
Aug-25-2025

Capacitive Touch HMI Interface | Durable & Ergonomic Control
Aug-24-2025

Capacitive Panel OEM Manufacturers – Custom Touchscreen Solutions
Aug-24-2025
Get a Free Quote
✔ 16 Years Manufacture Service ★★★★★
✔ 3 Technical Experts And 52+ Project Engineers Will Assiste You
✔ Wanty Employs Over 52 Engineers, Many Of Whom Come From Leading Tft Lcd Module Companies Such As Tianma And Boe-Varitronix. Each Core Team Member Brings 15 Years Of Industry Experience.
✔ If you would like more information about our products and services, please contact us. Whether you need a standard solution or a customized one, we are here to meet your needs.
✔ Please complete the form below, and the selected location will contact you promptly. Thank you for visiting, and have a great day!
